In an era where facts no longer matter, consequences still do
Over the last few years, we have written extensively about the strength of peoples’ beliefs and how difficult it is to change them. In spite of this, I thought we were making progress with a push to more evidence-based decision making. For something as polarizing as nuclear power, facts-based decision making is critical to increasing support. (I understand the paradigm of fear of radiation is more emotional than fact based and I agree that we need to appeal to emotions to create the change we need – but let’s leave that to a future discussion. In any case it certainly doesn’t hurt to have the facts on your side.)
With the populist surge in 2016 we have seen an accompanying rise in complete disregard for facts; all the way to the propagation of absolute lies (or “alternative facts”) to support peoples’ beliefs. I don’t want to get into a political discussion nor take sides on right versus left. What I do want to do in today’s post is to discuss something more fundamental – i.e. that although we are free to believe what we want – that beliefs have consequences – and that consequences matter.
So, let’s look at what happens when countries believe they can eliminate nuclear power from the mix and replace it with more wind and solar power. Of course, I am talking about Germany. Reducing carbon emissions is a reasonable goal as evidence (alternative facts notwithstanding) shows that climate change is impacting our environment and has long-term implications for our entire society. On the other hand, removing a low-cost low-carbon source of energy like nuclear power because of safety concerns is based on a strong element of fear rather than evidence. In fact, Germany’s nuclear plants are likely some of the safest in the world and there is no reason to suspect they will result in a catastrophic accident that means the end of Germany as we know it – yet that is what people fear.
So, what happens in a case like this? The results are in. Fossil fuel use is increasing in Germany, carbon emissions are going up and so is the cost of energy. The German people are paying more money for an outcome that does more damage to the environment and hence, their health. Frankly, it’s a high price to pay for the piece of mind that comes from eliminating the perceived risk of nuclear. Or in other words, the extreme fear of nuclear is driving policy more than concern for either energy cost or the environment.
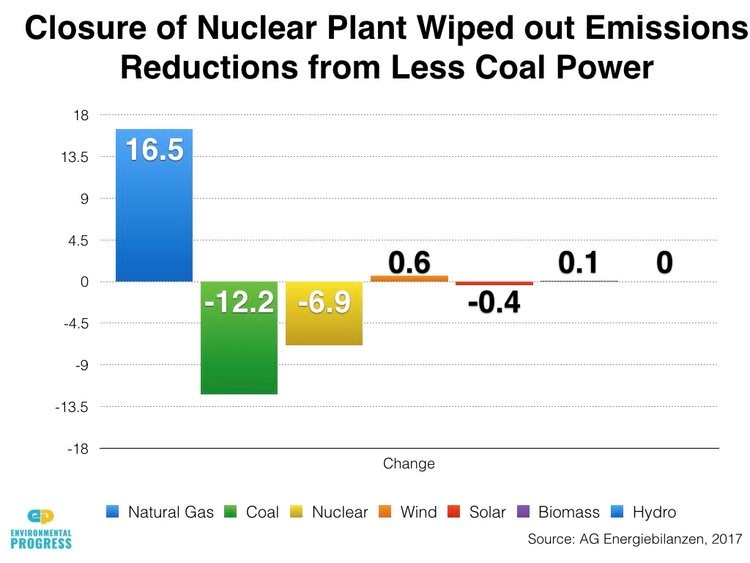
As shown above, closure of another nuclear plant in 2015 resulted in increased emissions in 2016 (the first full year it was out of service) even though there was a substantial substitution of gas to replace coal.
And after adding 10 percent more wind turbine capacity and 2.5 percent more solar panel capacity between 2015 and 2016, less than one percent more electricity from wind and one percent less electricity from solar was generated in 2016. So, not only did new solar and wind not make up for the lost nuclear, the percentage of time during 2016 that solar and wind produced electricity declined dramatically. And why was this the case? Very simply because Germany had significantly less sunshine and wind in 2016 than 2015.
This analysis was done by Environmental Progress and shows that the intermittency of these renewable sources of electricity both throughout the day and from year to year mean that even huge increases in capacity of these forms of generation will continue to require fossil backup in the absence of nuclear power making 100% renewables an unachievable goal. Another study shows that to achieve a 100% renewable system in Germany would require a back-up system capable of providing power at a level of 89% of peak load to address the intermittency.
Comparing Germany to France, France has more than double the share of low carbon energy sources and Germany has more than twice the cost of energy as France.
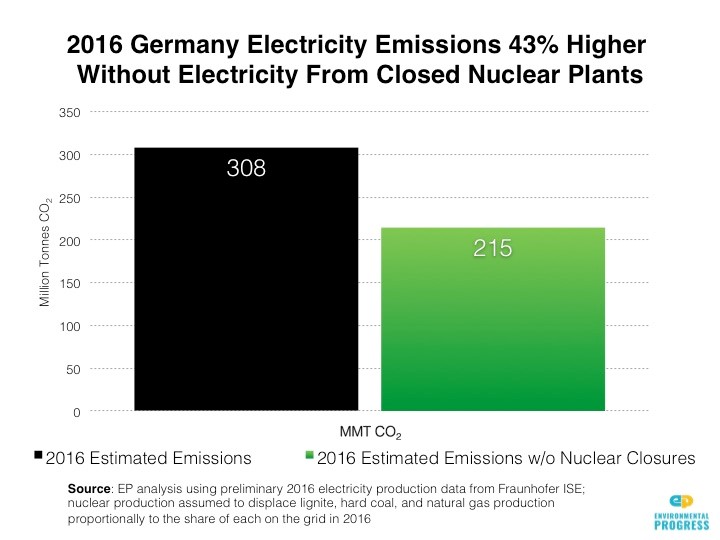
So, trying to decarbonize by also removing nuclear from the mix at the same time is simply too high a mountain to climb. The following shows that German emissions were 43% higher in 2016 without the nuclear plants that have been already shut down. Keep in mind that they still do have operating nuclear and with more plants to shut down, the future trend is not likely to change.
It’s not just about Germany. As Japan struggles to get its nuclear plants back on line after the 2011 Fukushima accident, its use of coal has skyrocketed. In 2015 its use of fossil fuels for electricity generation was 82% compared to 62% in 2010 when the nuclear plants were in operation. And now Japan plans to build 45 new coal plants (20 GW) over the next decade to meet its energy needs.
Finally, we can also look at South Australia, a nuclear free zone. Recent blackouts due in part to lower wind availability and the inability of thermal plants to make up the shortfall are also leading to questions on ‘how much renewables is too much’.
So, we can all continue to hold our beliefs very dearly and only listen to those that support them, while vilifying those that do not. However, please keep in mind that in a world where the farcical becomes reality, results still matter. And for now, the results are clear, taking nuclear power out of the mix in Germany is not achieving its political-planners’ goals. Yet these results are also not likely to change any German minds when it comes to nuclear power. But hey, why worry about the outcome when you know you are right or as said by comedian Chico Marx in the famous Marx brothers movie Duck Soup “Who you gonna believe – me or your own eyes?”?